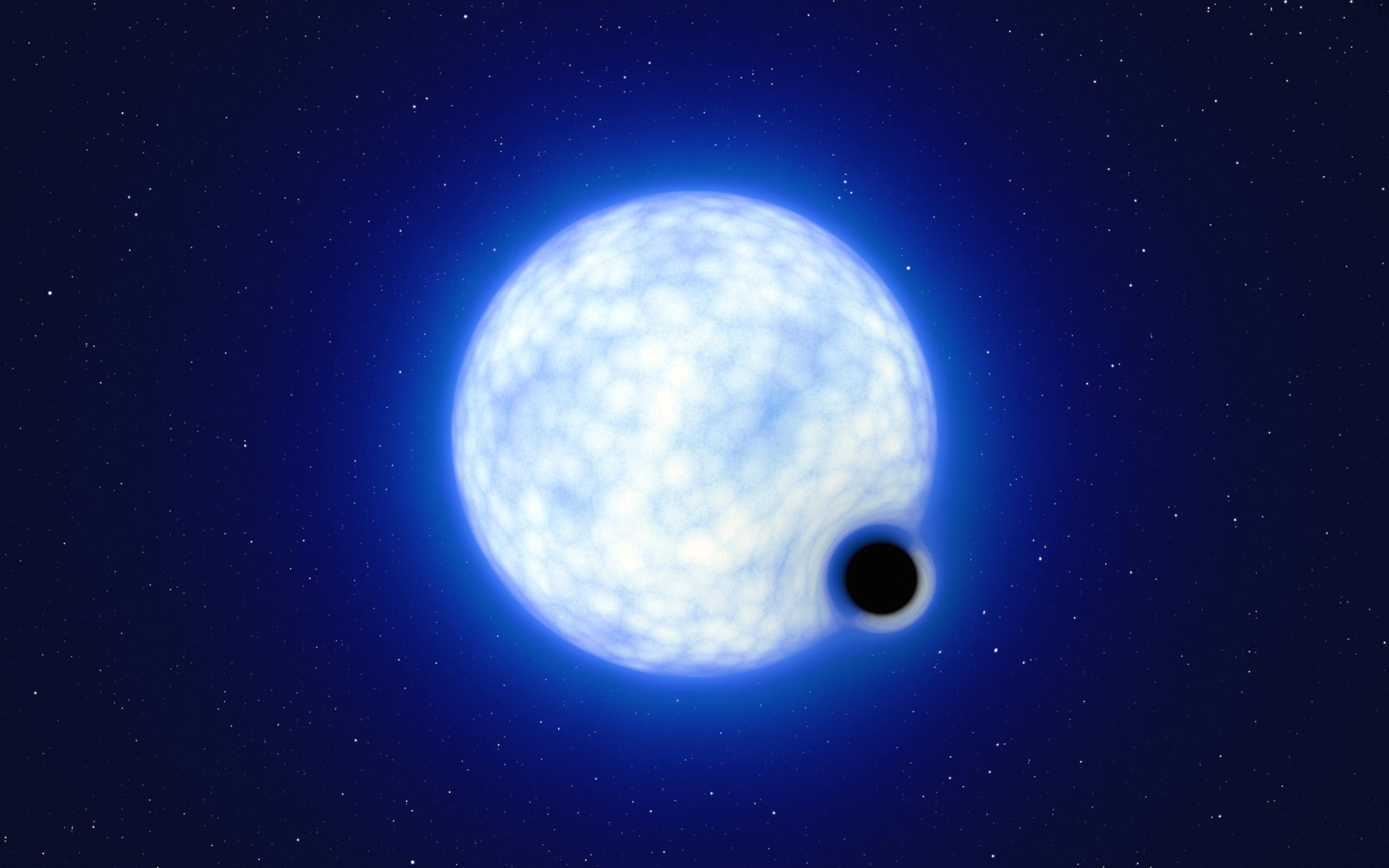
Researchers have discovered a dormant black hole outside the Milky Way.
The stellar-mass black hole has been observed in a neighbouring galaxy by a team of international scientists.
The newly found black hole is at least nine times the mass of the sun and orbits a hot blue star weighing 25 times the sun’s mass.

The star that gave rise to the black hole vanished without any sign of an associated supernova explosion, the study suggests.
Stellar-mass black holes are formed when massive stars reach the end of their lives and collapse under their own gravity.
In a system of two stars revolving around each other, this process leaves behind a black hole in orbit with a luminous companion star.
This black is considered dormant if it does not emit high levels of x-ray radiation, which is how such black holes are typically detected.
Dormant black holes are hard to spot as they do not interact much with their surroundings.
The researchers had been looking for black-hole-binary systems for more than two years and are particularly excited about the discovery, known as VFTS243.
Paul Crowther, professor of astrophysics at the University of Sheffield, said: “It’s a very exciting discovery.
“Although a number of dormant black hole candidates have been proposed, this is the first to be unambiguously detected outside our galaxy.”

As part of the research team, Professor Crowther has been working with the Institute of Physic and Astronomy’s Tomer Shenar, who started the study at KU Leuven in Belgium and is now a Marie-Curie Fellow at Amsterdam University in the Netherlands.
Dr Shenar said: “We identified a needle in a haystack.
“The star that formed the black hole in VFTS 243 appears to have collapsed entirely, with no sign of a previous explosion.
“Evidence for this direct-collapse scenario has been emerging recently, but our study arguably provides one of the most direct indications.
“This has enormous implications for the origin of black-hole mergers in the cosmos.”
The black hole in VFTS 243 was found using six years of observations of the Tarantula Nebula by the Fibre Large Array Multi Element Spectrograph (Flames) instrument on the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope.
The study is published in Nature Astronomy.